Economic Weaker Section (EWS) Reservation Eligibility
Those candidates who are financially backward and excluded from the other reservation schemes are the beneficiaries of 10% quota. Therefore, a reservation of 10% of seats in various government jobs and higher studies for the economically weaker sections has been implemented. The reservation came into force on January 14, 2019.
EWS Reservation – 124th amendment
The Economic Reservation Act amends articles 15 and 16 of the constitution.
With this amendment, a clause is added which allows states to make “special provisions”. The “special provisions” are for the advancement of financially backward sections of society.
The “special provisions” are related to admissions to educational institutions. These educational institutions include private educational institutes, aided and unaided educational institutes other than minority institutes.
Reservation System in India
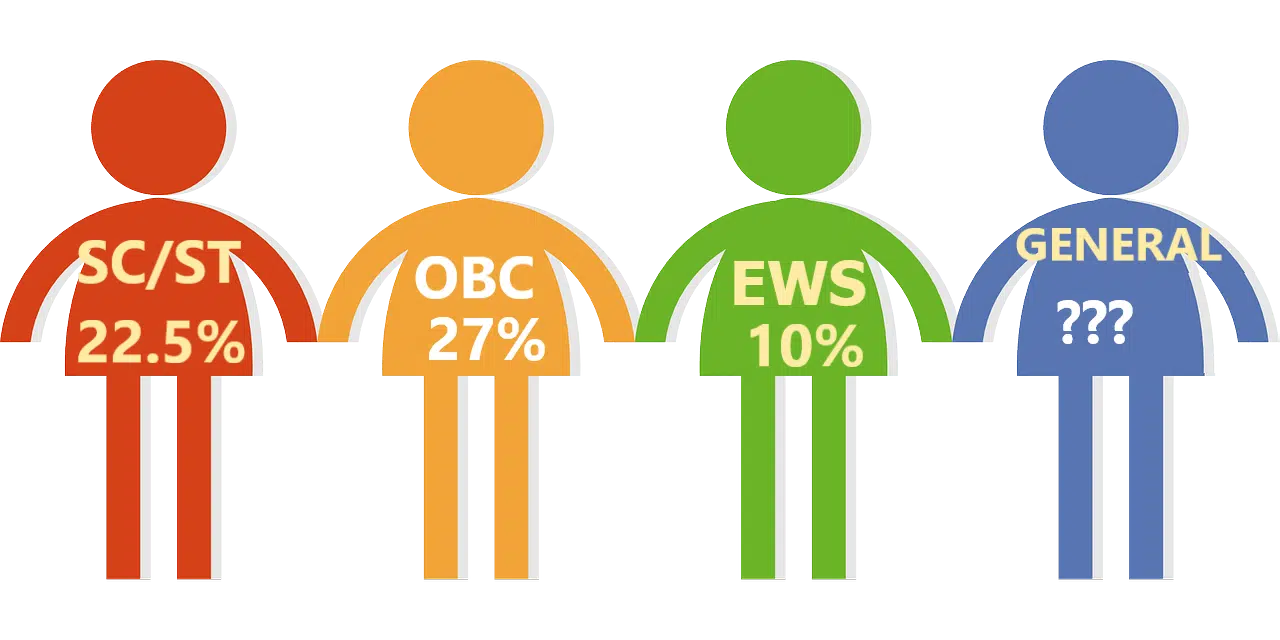
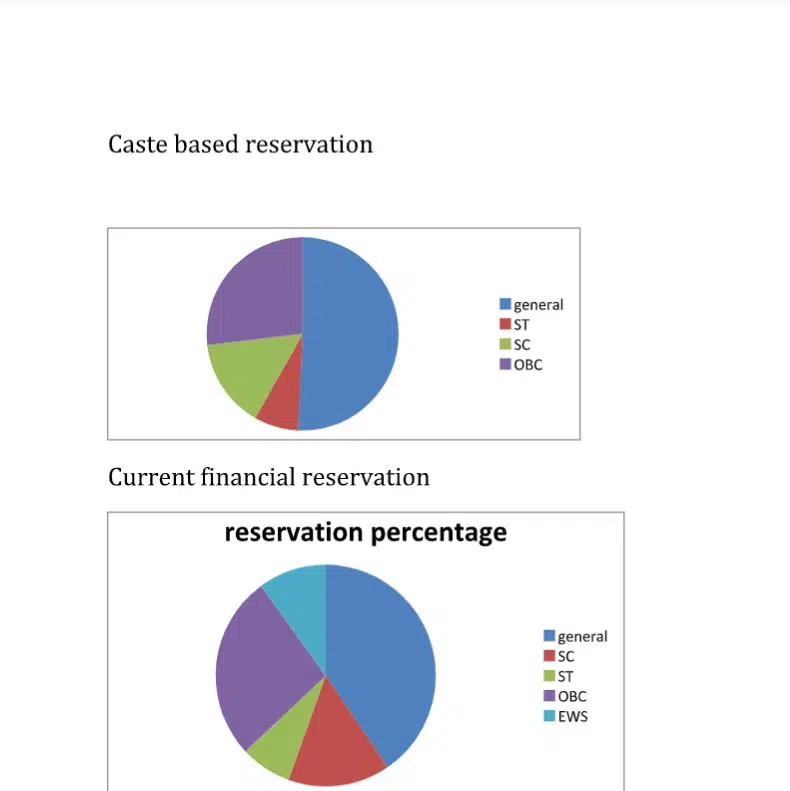
In India, a total of 49.5% of seats are reserved on the basis of caste. In other words, 22.5% of available seats are for SC and STs. Out of 22.5%, 7.5% and 15% reservations for STs scheduled castes [SCs] respectively. Further, 27% is allocated for other backward classes [OBC]. In addition to this, reservations based on financial status were added which ultimately increased the reservation seats to 59.5%. However, there is a decrease in the open category or merit seats from 50.5% to 40.5%.
Why there is an EWS Reservation?
It is an undeniable fact that caste-based reservation comprises nearly 50% of seats in government jobs and educational sector. However, there are huge proportions of the upper class population who live in poverty. Moreover, these people cannot claim reservations due to their higher caste instead of being poor. In fact, it is the first time in the Indian history that the nation made non-caste and non-religion based reservation.
Who are the beneficiaries of this EWS Reservation Bill?
The eligibility criteria cover almost 80% of the population. However, the 10% quota is mainly for the poorer sections of upper-class Hindus and other religions.
The Brahmins, Rajputs, Jats, Vaishyas, Marathas, Patels, kappus and Kammas are the major upper-class Hindus who benefit from the reservation.
The economically weak among other religions such as Muslims and Christians can also benefit from the economic reservation.
What are the criteria’s of EWS Reservation Eligibility?
The criterion that describes Economically Weaker Sections is based on their family income and the size of land they have. In other words, a person is eligible for financial reservation, if he has an annual income of less than eight lakhs Indian rupees.
Further, if a person owns an agricultural land of less than 5 acres and the house is below 1000square feet.
In addition, if a person’s own residential land is not exceeding 100 yards in the municipal area and not more than 200 yards in the non-municipal area are also eligible.
1. Family income
Gross family income of less than eight lakhs rupees can benefit from the reservation, as they are identified as economically weaker sections [EWS].
Family income includes from all sources such as salary, business, agriculture, parent’s and spouse’s income.
2. Agricultural land.
People can claim financial reservation if a family’s total agricultural land is less than 5 acres. However, applying for EWS status, clubbing of family’s property in different locations.
Despite the fact of less than 5 acres of agricultural land ownership for EWS status, nearly 90% of the country’s population falls in this limit.
3. House of less than 1000 square feet
An individual can get a 10% reservation if his or her house if less than 1000 square feet. However, in India, more than 80% of houses are below 500 square feet.
4. Residential plot
If a person owns a residential plot of below 100 square yards in a municipal area is eligible for 10% reservation. Further, in the notified municipal area, it should not be more than 200 square yards.
EWS Eligibility Update
The Economic Weaker Section (EWS) reservation provides a 10% quota in government jobs and educational institutions for individuals from the general category who are not covered under other reservations (SC, ST, OBC). To qualify, candidates must meet specific criteria: their family’s gross annual income should be below ₹8 lakh, and they must not own certain assets, such as agricultural land of 5 acres or more, a residential flat of 1000 sq. ft. or more, or residential plots exceeding 100 sq. yards in notified municipalities.
The EWS reservation was introduced by the 103rd Constitutional Amendment in 2019 and has been upheld by the Supreme Court, most notably in the Janhit Abhiyan case of 2022. Despite ongoing debates about the income cap and exclusion of other reserved categories, the policy remains in force
Also read: UPSC Age Limit for UPSC Civil Services Exam
Who are not eligible for the EWS Reservation?
If a candidate belongs to a caste group that is already covered in the existing reservation system, the person is ineligible. For example, if a person belongs to SC or ST category, they can apply only under SC or ST Reservation Act.








Leave a Reply